Vitamins and minerals are often called micronutrients because your body needs only tiny amounts of them. Yet failing to get even those small quantities virtually guarantees disease.
Lack of energy, bad physical form, that little extra belly fat we noticed not so long age — these may all be symptoms of vitamins deficiency.
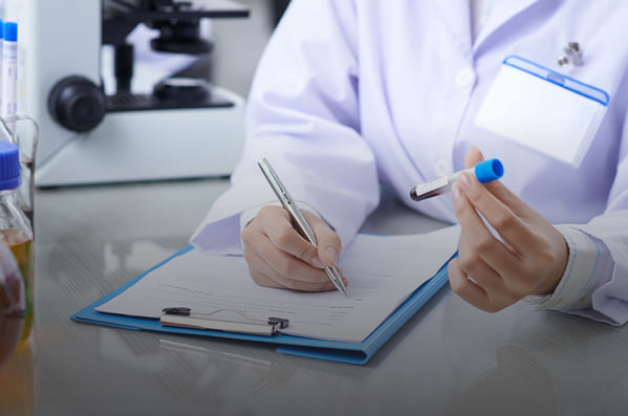
If you don’t want to risk developing diabetes, having a heart attack or stroke, So if you’re worried about your health, if your overall level of fitness, including sexual performance, if you don’t engage in any sport activities, or if you lead a sedentary lifestyle, you are strongly encouraged to undergo Screening for vitamins profile.
Vitamins, minerals and enzymes: major role in health & disease prevention
Vitamins and minerals play a different kind of role in energy metabolism; they are required as functional parts of enzymes involved in energy release and storage. Vitamins and minerals that make up part of enzymes are referred to as coenzymes and cofactors, respectively.
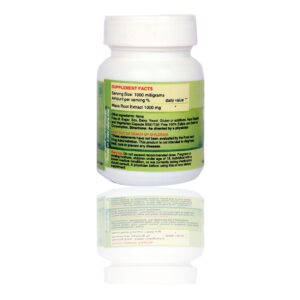
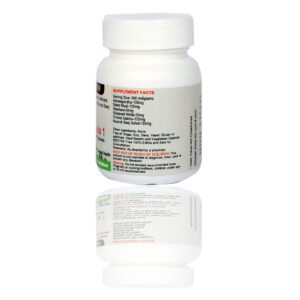
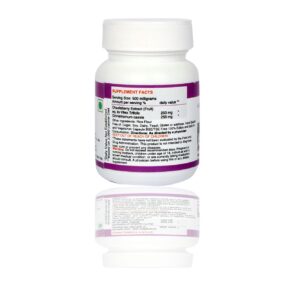
This package we do 14 vital vitamins which helps in over all health, metabolism, disease prevention, energy, performance etc
VITAMINS: D, D2, D3, A, B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, B12, E, K, few vitamins are explained its importance
Role of vitamin D in human metabolic processes
Vitamin D is required to maintain normal blood levels of calcium and phosphate, that are in turn needed for the normal mineralisation of bone, muscle contraction, nerve conduction, and general cellular function in all cells of the body.
Role of vitamin A in human metabolic processes
Vitamin A (retinol) is an essential nutrient needed in small amounts by humans for the normal functioning of the visual system; growth and development; and maintenance of epithelial cellular integrity, immune function, and reproduction. These dietary needs for vitamin A are normally provided for as preformed retinol (mainly as retinyl ester) and pro-vitamin A carotenoids.
Role of vitamin B12 in human metabolic processes
Vitamin B-12 is the largest and most structurally complicated vitamin. It occurs naturally in meat products and can only be industrially produced through bacterial fermentation synthesis.
Vitamin B-12 can be found naturally in animal products, such as fish, meat, eggs, and dairy products. It does not typically occur in plant foods.
Vitamin B-12 is crucial to the normal function of the brain and the nervous system. It is also involved in the formation of red blood cells and helps to create and regulate DNA.
The metabolism of every cell in the body depends on vitamin B-12, as it plays a part in the synthesis of fatty acids and energy production. Vitamin B-12 enables the release of energy by helping the human body absorb folic acid.
Role of vitamin B6 in human metabolic processes
Vitamin B6 plays a role in the metabolism of protein, carbohydrates and fats, the production of neurotransmitters and the formation of nicotinic acid. It is vital for maintaining a healthy nervous system, skin, muscles and blood. One of the central roles of this vitamin is in protein metabolism where it helps regulate the balance of amino acids in the body. It is also closely involved in hormone production.
Role of vitamin E in human metabolic processes
- It is an antioxidant. This means it protects body tissue from damage caused by substances called free radicals. Free radicals can harm cells, tissues, and organs. They are believed to play a role in certain conditions related to aging.
- The body also needs vitamin E to help keep the immune system strong against viruses and bacteria. Vitamin E is also important in the formation of red blood cells. It helps the body use vitamin K. It also helps widen blood vessels and keep blood from clotting inside them.
- Cells use vitamin E to interact with each other. It helps them carry out many important functions.
Role of folate in human metabolic processes
Folate is the natural form of vitamin B9, water-soluble and naturally found in many foods. It is also added to foods and sold as a supplement in the form of folic acid; this form is actually better absorbed than that from food sources—85% vs. 50%, respectively. Folate helps to form DNA and RNA and is involved in protein metabolism. It plays a key role in breaking down homocysteine, an amino acid that can exert harmful effects in the body if it is present in high amounts. Folate is also needed to produce healthy red blood cells and is critical during periods of rapid growth, such as during pregnancy and fetal development.